| You are here: Almanahj Website ⇒ American curriculum ⇒ 10th Grade ⇒ Geology ⇒ Term 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
Worksheet about EARTHS LAYERS AND TECTONIC PLATES | ||
|---|---|---|
| Subject: Geology | ||
| 10th Grade | ||
| Term 1 | ||
| Year: 2023/2024 | ||
| Size: 808.2KB | ||
| Number of clicks: 157 | ||
| Publish date:November 28, 2023 | ||
| Added by: Eman | ||
| Last download date: 2024-09-03 06:46:14 | By: theodor Paula Andrea Ruiz | |
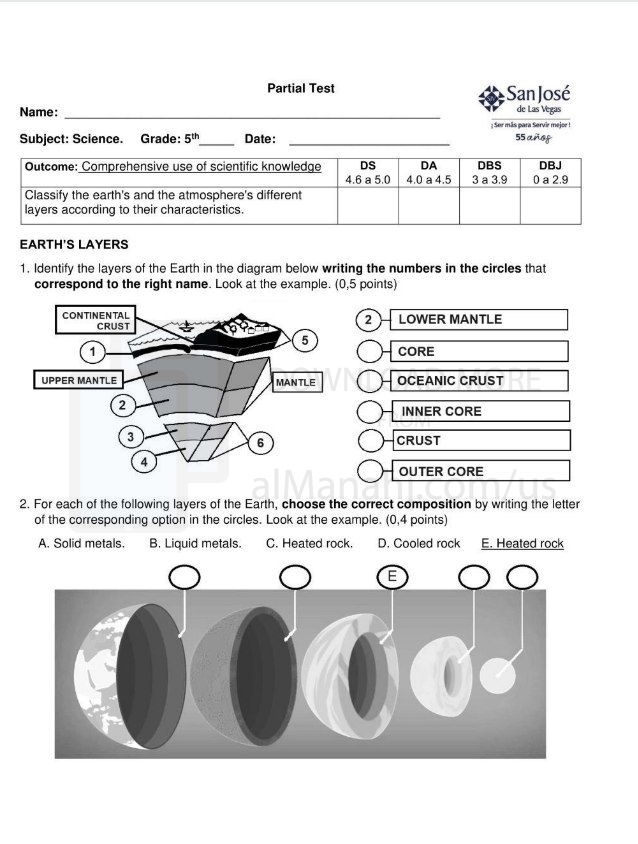
| File info: Earth's Layers: The Earth is composed of several layers, each with distinct properties and compositions. From the innermost to the outermost layers, they are: 1. Inner Core: The innermost layer of the Earth, located at the center. It is a solid sphere primarily made of iron and nickel. The inner core is under extreme pressure and has temperatures estimated to be around 5,000-6,000 degrees Celsius (9,000-10,800 degrees Fahrenheit). 2. Outer Core: Surrounding the inner core is the outer core. It is a liquid layer predominantly composed of molten iron and nickel. The outer core is responsible for generating Earth's magnetic field through a process called geodynamo. 3. Mantle: The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles). It is composed of solid rock and is divided into the upper mantle and the lower mantle. The upper mantle is rigid and forms part of the lithosphere, while the lower mantle is more ductile and capable of slow flow over long periods of time. 4. Crust: The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth and is the thinnest layer. It is composed primarily of solid rock and is divided into two types: continental crust and oceanic crust. The continental crust is generally thicker and less dense than the oceanic crust, which is thinner and denser. Tectonic Plates: Tectonic plates are large, rigid pieces of the Earth's lithosphere that fit together to form the Earth's surface. These plates are constantly moving, albeit very slowly, and interact with each other at their boundaries. The study of these plates and their interactions is known as plate tectonics. The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several major tectonic plates, including the Eurasian Plate, African Plate, North American Plate, South American Plate, Pacific Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, and Antarctic Plate, among others. These plates cover the Earth's surface and vary in size. The boundaries between tectonic plates are the areas where their interactions occur. There are three main types of plate boundaries: 1. Divergent Boundaries: Plates move away from each other at divergent boundaries. This results in the upwelling of magma from the mantle, creating new crust and causing the formation of mid-ocean ridges. Divergent boundaries can also occur on land, resulting in rift valleys. 2. Convergent Boundaries: Plates collide with each other at convergent boundaries. There are three types of convergent boundaries: oceanic-oceanic convergence, oceanic-continental convergence, and continental-continental convergence. These collisions can lead to the formation of mountain ranges, volcanic activity, and subduction zones. 3. Transform Boundaries: Transform boundaries occur where plates slide past each other horizontally. These boundaries are characterized by large faults and can result in earthquakes. The movement and interactions of tectonic plates are driven by mantle convection, which is the transfer of heat within the Earth's mantle. The study of tectonic plates and plate boundaries is crucial for understanding Earth's geology, the distribution of continents, the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic activity, and the overall dynamics of our planet. | ||
| Downloading link Worksheet about EARTHS LAYERS AND TECTONIC PLATES |
|---|
|
1701175986.pdf
The file is being prepared for download
|
| File images |
|---|
 |