| You are here: Almanahj Website ⇒ American curriculum ⇒ 3rd Grade ⇒ Geology ⇒ Term 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
Worksheet about The sun moon and earth | ||
|---|---|---|
| Subject: Geology | ||
| 3rd Grade | ||
| Term 1 | ||
| Year: 2023/2024 | ||
| Size: 406.3KB | ||
| Number of clicks: 154 | ||
| Publish date:November 26, 2023 | ||
| Added by: Eman | ||
| Last download date: 2024-09-13 12:51:00 | By: theodor Maria Jose Crespo Rodas | |
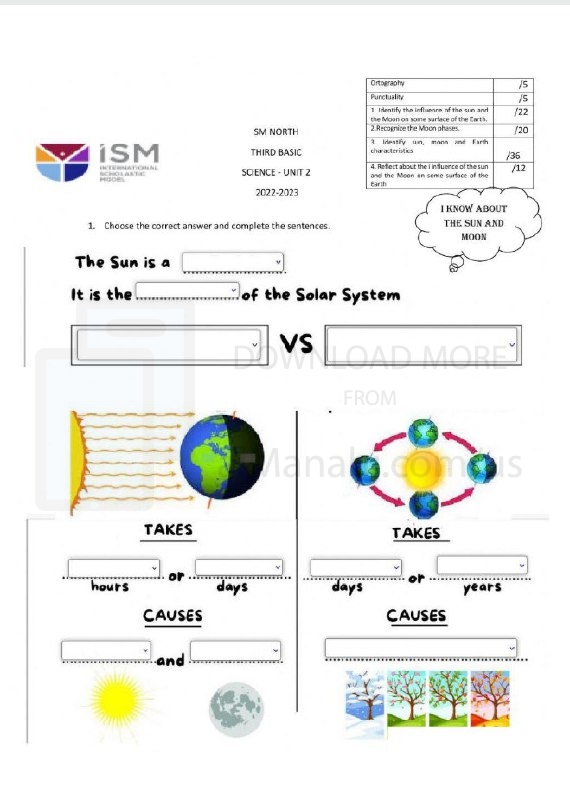
| File info: The Sun, Moon, and Earth are three celestial bodies that have a significant impact on each other and play key roles in various astronomical and natural phenomena. Here's an overview of their characteristics and interactions: 1. Sun: The Sun is a star, located at the center of our solar system. It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium and generates energy through nuclear fusion. The Sun's immense gravity holds the planets, including Earth, in orbit around it. It radiates light and heat, providing energy that sustains life on Earth. The Sun also influences Earth's climate and weather patterns through its radiation, solar wind, and magnetic activity. 2. Earth: Earth is the third planet from the Sun and is the only known celestial body to support life. It has a diverse range of ecosystems and a dynamic geology. The Earth's rotation on its axis causes day and night, while its orbit around the Sun determines the annual cycle of seasons. The Earth's atmosphere protects the planet from harmful solar radiation and plays a crucial role in regulating temperatures and supporting life. 3. Moon: The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and is the fifth-largest moon in the solar system. It orbits the Earth, taking approximately 27.3 days to complete one revolution. The Moon's gravitational pull causes ocean tides on Earth due to its interaction with the Earth's oceanic and continental masses. The Moon also has a significant influence on Earth's axial tilt, which affects our planet's climate and seasons. Interactions and Phenomena: The interactions between the Sun, Moon, and Earth lead to various astronomical and natural phenomena. Here are a few examples: 1. Solar and Lunar Eclipses: Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, blocking the Sun's light and casting a shadow on the Earth's surface. Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Earth's shadow to fall on the Moon. 2. Tides: The gravitational interaction between the Moon and Earth causes ocean tides. The Moon's gravitational pull creates a tidal bulge on the side of the Earth facing the Moon and a second bulge on the opposite side. These tidal bulges result in the regular rise and fall of ocean water levels, known as high tides and low tides. 3. Seasons: The tilt of the Earth's axis relative to its orbit around the Sun leads to the changing seasons. As the Earth orbits the Sun, different parts of the planet receive varying amounts of sunlight, leading to variations in temperature and weather patterns throughout the year. 4. Solar Wind and Magnetosphere: The Sun emits a constant stream of charged particles called the solar wind. Earth's magnetosphere, a region of its magnetic field, interacts with the solar wind, deflecting and trapping many of these particles. This interaction creates phenomena like auroras (Northern and Southern Lights) near the Earth's poles. The Sun, Moon, and Earth form an interconnected system, influencing each other in various ways and contributing to the astronomical and natural phenomena we observe. | ||
| Downloading link Worksheet about The sun moon and earth |
|---|
|
1701006272.pdf
The file is being prepared for download
|
| File images |
|---|
 |