| You are here: Almanahj Website ⇒ American curriculum ⇒ 8th Grade ⇒ Geology ⇒ Term 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
Worksheet about Earth systems | ||
|---|---|---|
| Subject: Geology | ||
| 8th Grade | ||
| Term 1 | ||
| Year: 2023/2024 | ||
| Size: 300.2KB | ||
| Number of clicks: 132 | ||
| Publish date:November 24, 2023 | ||
| Added by: Eman | ||
| Last download date: 2024-09-13 16:11:03 | By: theodor eslamahmedkhalil | |
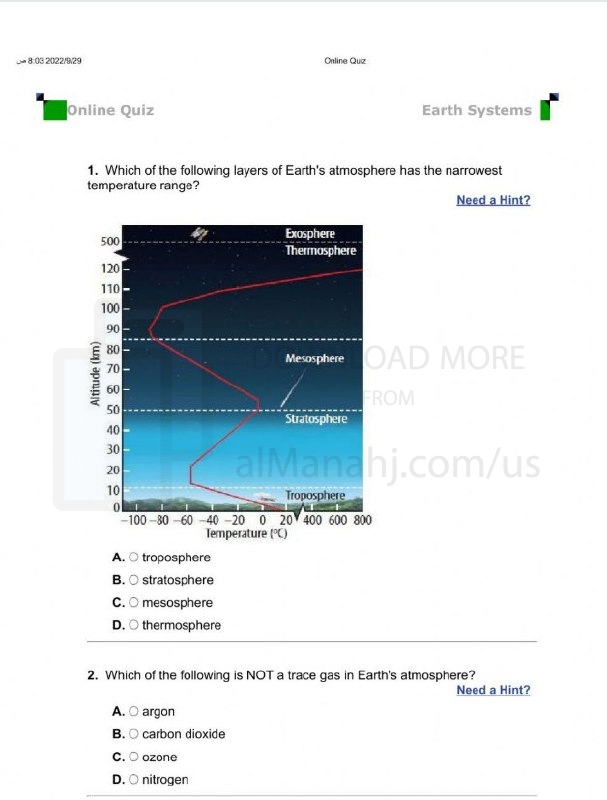
| File info: The Earth can be viewed as a complex system consisting of several interconnected Earth systems. These systems are dynamic and interact with one another, shaping the overall functioning of the planet. The main Earth systems include: 1. Geosphere: The geosphere refers to the solid Earth, including the rocks, minerals, and landforms that make up the planet's surface. It encompasses the lithosphere (the rigid outer layer of the Earth), the asthenosphere (the partially molten and ductile layer beneath the lithosphere), and the Earth's interior, including the mantle and core. The geosphere is involved in geological processes such as plate tectonics, volcanic activity, erosion, and the formation of landforms. 2. Atmosphere: The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the Earth. It includes the troposphere (closest to the Earth's surface), stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. The atmosphere plays a crucial role in regulating climate, weather patterns, and the distribution of heat and energy. It is involved in processes such as atmospheric circulation, the greenhouse effect, and the formation of weather phenomena like clouds, storms, and precipitation. 3. Hydrosphere: The hydrosphere encompasses all of Earth's water, including oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, groundwater, and atmospheric water vapor. It plays a vital role in the water cycle, which involves the movement of water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans through processes like evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, and infiltration. The hydrosphere influences climate, shapes landscapes through erosion and deposition, and supports diverse aquatic ecosystems. 4. Biosphere: The biosphere includes all living organisms on Earth and their interactions with the other Earth systems. It encompasses ecosystems on land, in water, and even within the atmosphere. The biosphere relies on the geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere for resources such as nutrients, water, and energy. It plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling, oxygen production, food webs, and the regulation of Earth's overall biogeochemical processes. 5. Cryosphere: The cryosphere refers to the frozen parts of the Earth, including ice caps, glaciers, ice sheets, snow cover, and permafrost. It interacts with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere, influencing climate patterns, sea level rise, and regional water availability. Changes in the cryosphere have significant implications for global climate dynamics and ecosystems. These Earth systems are interconnected and operate through complex feedback mechanisms. Changes in one system can have cascading effects on the others, leading to Earth's dynamic behavior and the occurrence of natural processes such as climate change, geological events, and ecosystem shifts. Understanding the interactions and dynamics of these Earth systems is crucial for comprehending the functioning of our planet and addressing environmental challenges. | ||
| Downloading link Worksheet about Earth systems |
|---|
|
1700835076.pdf
The file is being prepared for download
|
| File images |
|---|
 |