| You are here: Almanahj Website ⇒ American curriculum ⇒ 9th Grade ⇒ Chemistry ⇒ Term 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
Worksheet about Cleavage in organic chemistry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Subject: Chemistry | ||
| 9th Grade | ||
| Term 1 | ||
| Year: 2023/2024 | ||
| Size: 267.3KB | ||
| Number of clicks: 108 | ||
| Publish date:November 06, 2023 | ||
| Added by: Eman | ||
| Last download date: 2024-08-22 02:39:35 | ||
| Updated by: Eman9966 on 2023-11-06 11:16:39 | By: theodor sapiyan kandong | |
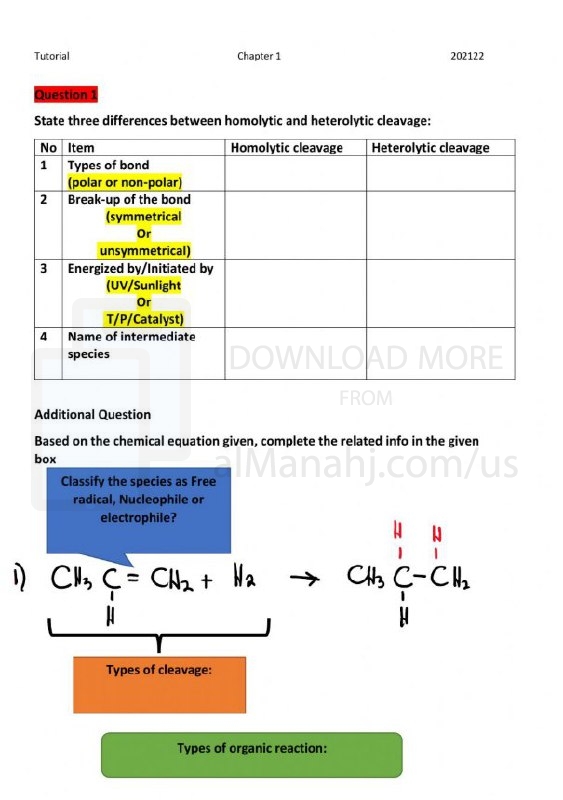
| File info: In organic chemistry, the term "cleavage" refers to the breaking of chemical bonds within a molecule. It involves the separation of a larger molecule into smaller fragments or functional groups. Cleavage reactions are essential in organic chemistry as they allow chemists to manipulate and transform complex molecules into simpler compounds. Cleavage reactions can occur through various mechanisms, and the choice of the reaction depends on the specific functional groups present in the molecule and the desired outcome. Here are some common types of cleavage reactions in organic chemistry:1. Homolytic Cleavage: In homolytic cleavage, the bond between two atoms is broken, and each atom retains one electron from the bond. This process forms two highly reactive species called radicals. Homolytic cleavage is typically initiated by the input of energy, such as heat or light. It is commonly observed in free-radical reactions. 2. Heterolytic Cleavage: Heterolytic cleavage involves the breaking of a bond between two atoms, resulting in the formation of two charged species, namely ions. One atom retains both electrons from the bond, acquiring a negative charge (anion), while the other atom becomes positively charged (cation). Heterolytic cleavage is prevalent in ionic reactions and reactions involving polar molecules. 3. Bond Cleavage by Acid or Base: Cleavage can also occur as a result of acid or base-catalyzed reactions. Acids can donate protons (H+) to weaken or break a bond, while bases can accept protons and facilitate bond cleavage. Acid-catalyzed cleavage is commonly observed in reactions such as hydrolysis, where a bond is broken by the addition of water in the presence of an acid. 4. Bond Cleavage by Oxidation or Reduction: Cleavage reactions can be induced by oxidation or reduction processes. Oxidation involves the loss of electrons, while reduction involves the gain of electrons. These reactions can cause changes in the bonding pattern of a molecule, leading to the cleavage of specific bonds. 5. Bond Cleavage by Photolysis: Photolysis refers to the cleavage of bonds induced by light energy. Light of a specific wavelength can excite electrons in a molecule, leading to the breaking of a bond. Photolysis is often used in organic synthesis to generate reactive intermediates or to break specific bonds selectively. Cleavage reactions in organic chemistry are powerful tools for synthesizing new compounds, studying reaction mechanisms, and understanding the structure and reactivity of organic molecules. They are essential for the design and development of new drugs, materials, and functional molecules. | ||
| Downloading link Worksheet about Cleavage in organic chemistry |
|---|
|
1699269355.pdf
The file is being prepared for download
|
| File images |
|---|
 |