| You are here: Almanahj Website ⇒ American curriculum ⇒ 12th Grade ⇒ Chemistry ⇒ Term 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
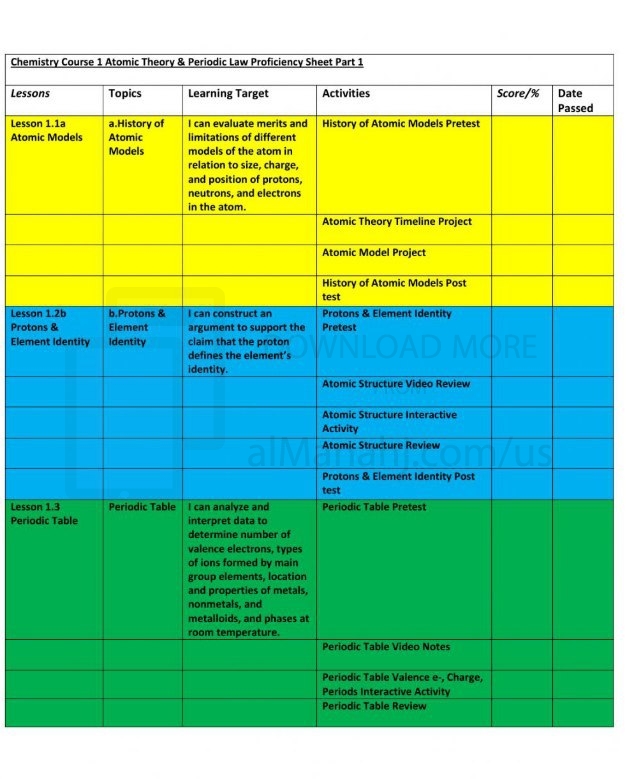
Worksheet about Atomic theory | ||
|---|---|---|
| Subject: Chemistry | ||
| 12th Grade | ||
| Term 1 | ||
| Year: 2023/2024 | ||
| Size: 352.6KB | ||
| Number of clicks: 56 | ||
| Publish date:November 04, 2023 | ||
| Added by: Eman | ||
| Last download date: 2024-09-12 06:21:29 | ||
| Updated by: Eman9966 on 2023-11-04 12:08:16 | By: theosor Coach Spivey | |
| File info: Info Atomic theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the nature and behavior of atoms, which are the building blocks of matter. The atomic theory provides a framework for understanding the structure, properties, and interactions of elements and compounds. Here is a description of the key components of atomic theory:1. Elements and Atoms: The atomic theory states that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. Each element is made up of one type of atom characterized by its unique properties. Atoms are indivisible and cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions. 2. Subatomic Particles: Atoms are composed of subatomic particles, namely protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge (neutral), and electrons have a negative charge. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom, while electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. 3. Atomic Structure: The atomic theory explains the structure of an atom. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, which account for most of the atom's mass. The electrons occupy energy levels around the nucleus, with each energy level accommodating a specific number of electrons. 4. Atomic Number and Mass: The atomic number of an element corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus, defining the element's identity. The mass number represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. 5. Isotopes: Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and, consequently, different mass numbers. Isotopes have similar chemical properties but may differ in stability and nuclear properties. 6. Electron Configuration: The arrangement of electrons in the energy levels or shells of an atom is called its electron configuration. The distribution of electrons determines the chemical behavior and reactivity of an element. 7. Chemical Bonding: Atomic theory explains how atoms interact to form chemical bonds. Atoms can gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This leads to the formation of compounds through various types of bonding, such as ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. 8. Conservation of Mass: The atomic theory supports the principle of conservation of mass, which states that the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the products. This principle is based on the fact that atoms are neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. Atomic theory has evolved over time, with contributions from scientists such as John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, and many others. It provides a foundation for understanding the behavior of matter at the atomic and molecular levels, enabling scientists to explain and predict chemical reactions, properties of elements, and the structure of compounds. | ||
| Downloading link Worksheet about Atomic theory |
|---|
|
1699099454.pdf
The file is being prepared for download
|
| File images |
|---|
 |